Due to increased environmental awareness, the shift towards renewable energy sources is noticeably accelerating, providing green alternatives to conventional electricity generation. Wind and solar power are leading this green energy wave. We can harness nature’s abundance to make electricity and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
To determine which source suits diverse uses, we’ll examine their initial setup costs, efficiency rates, ecological footprints, and expansion potential.
Solar energy, characterized by its utilization of the sun’s rays, has recently enjoyed popularity. Its reasonable pricing and widespread accessibility make it a favored option for household and business ventures. Wind energy, which utilizes the wind’s kinetic energy, has experienced notable growth, primarily due to wind farms and turbines.
Learn how solar and wind energy differ to choose the right renewable energy source.
What is wind power?
Wind power, as indicated by its name, utilizes the natural movement of wind to create electricity. The components of a wind turbine, encompassing rotor blades and a tower, grasp the wind’s energy and morph it into a spinning motion. This motion is subsequently converted to electrical energy through a generator.
A prominent benefit of wind power lies in its adaptability in scale. Wind farms can span from petite setups serving individual homes to expansive undertakings that energize whole communities. This adaptable nature makes wind power suitable for numerous environments, including rural landscapes and bustling urban areas.
Like solar energy, wind power stands as a green and renewable energy source. It operates without releasing greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air, positioning it as a green alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Further, once the turbines are erected, the operational costs associated with wind power are reasonably low, given that the wind, its fuel source, comes at no cost.
Wind power, however, has its downsides. Wind turbines’ performance is closely linked to the presence and steadiness of wind, factors that vary by location and weather. Turbines create noise and interfere with landscape aesthetics, potentially making them less favorable for specific settings. Moreover, the upfront expenses associated with setting up wind turbines can be substantial, coupled with a necessity for periodic upkeep to maintain peak functionality.
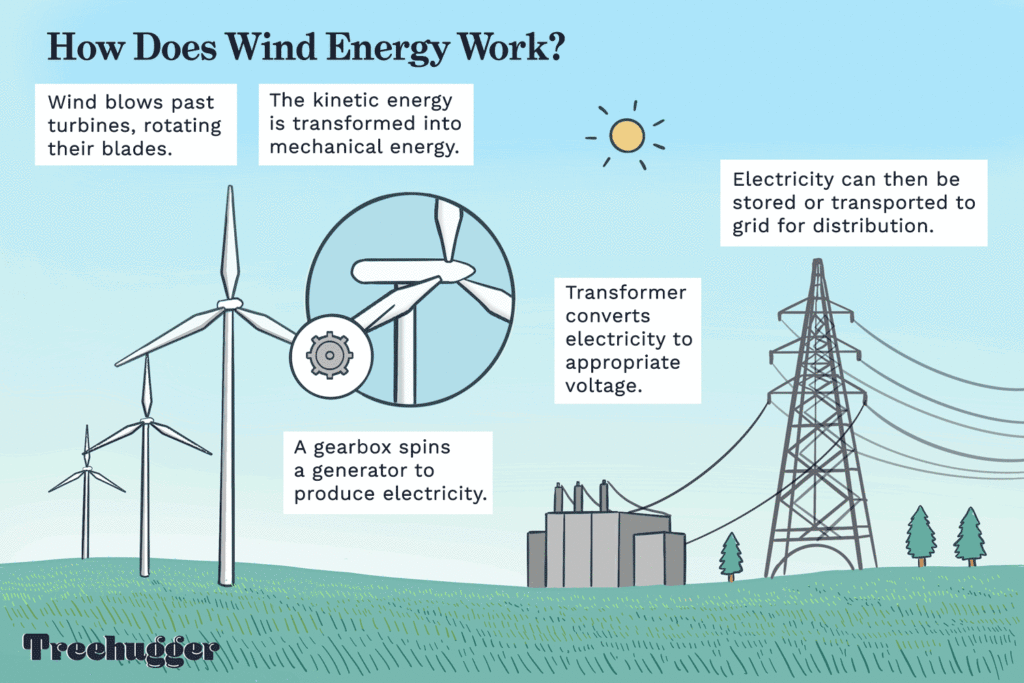
Credit: treehugger.com
Advantages of Wind Power
- Environmentally Friendly: Wind power does not emit greenhouse gases or pollute the air, contributing to the fight against climate change and lessening ecological degradation.
- Flexible Scaling: The extent of wind farms can vary greatly, from modest setups to extensive ventures, allowing wind power to be adaptable for many uses.
- Economical in the Long Run: After the setup phase, the ongoing costs associated with wind turbines are quite low because wind, its energy source, is naturally occurring and cost-free.
- Boosts Employment and Economic Growth: The sector associated with wind power fosters job opportunities and positively influences local economies, especially in regions endowed with substantial wind assets.
Disadvantages of Wind Power
- Dependency on Wind Conditions: The performance efficiency of wind turbines is contingent upon the regularity and presence of wind, elements subject to alterations based on geographical location and weather patterns.
- Auditory and Visual Disturbance: During their operation, wind turbines can create noise and may disrupt the natural vista, factors that might not be appreciated in every locale.
- Substantial Upfront Expenditure: The inception phase of wind turbines necessitates a sizable financial outlay, including turbine procurement and the requisite foundational structures.
- Potential Threat to Wildlife: Wind turbines can endanger avian and bat species, primarily if situated along migratory paths or within vital habitats.
What is solar energy?
Solar energy revolves around transforming sunlight into electricity, either via photovoltaic (PV) panels or through solar thermal systems. PV panels, constructed with solar cells, capture sunlight and directly change it into electricity through the photovoltaic phenomenon. Conversely, solar thermal systems harness the sun’s warmth to produce electricity or generate hot water or steam.
A standout benefit of solar energy lies in its inexhaustibility. The sun incessantly showers our planet with energy, marking it as an incredibly sustainable and continuously renewable power source. Moreover, solar energy operates cleanly without releasing any detrimental emissions, making it a prime choice for those aiming to minimize their environmental impact and contribute to the fight against global warming.
Yet, solar energy has its challenges. The efficacy of solar systems is determined mainly by sunlight’s availability, which can be inconsistent due to shifting weather patterns and the specific geographic position of the installation. Additionally, there’s a notable upfront investment associated with installing solar panels, though it’s worth noting that these costs have consistently declined over recent times. Solar energy’s affordability and reach have grown significantly despite these challenges, particularly in household and business implementations.
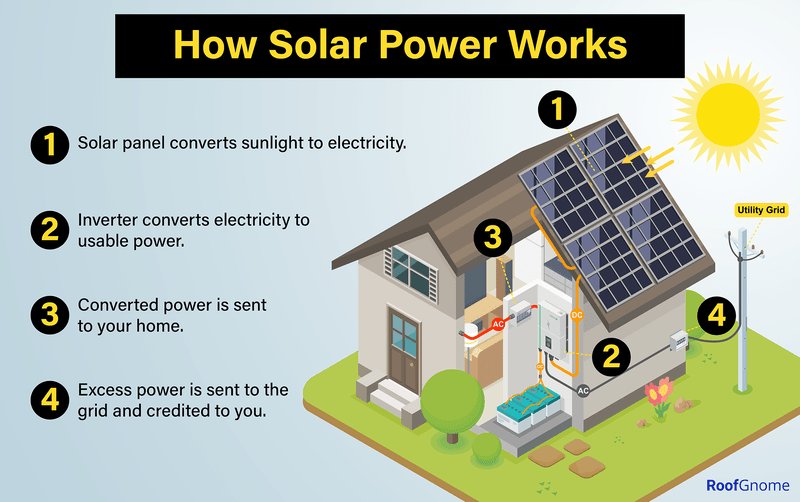
Credit: roofgnome.com
Advantages of Solar Energy
- Ever-renewing Source: Solar energy is an endlessly renewable and sustainable power option due to the sun’s relentless output.
- Eco-friendly Operation: Solar energy doesn’t release greenhouse gases or other airborne contaminants, enabling a shift away from fossil fuels and reducing ecological harm.
- Ubiquitous Presence: Solar energy can be captured in various settings due to its ubiquitous presence.
- Financial Benefits: Solar panels can substantially reduce electricity expenses after the setup phase, leading to long-lasting economic advantages.
Disadvantages of Solar Energy
- Dependency on Sunlight: The productivity of solar energy hinges on the regularity and intensity of sunlight, which external factors like climatic variations and geographic positioning can influence.
- Notable Initial Outlay: Even though the price tag of solar panels has declined, the initial expenditure remains relatively high for many.
- Requirement of Ample Space: Effective deployment of solar panels demands sufficient space, posing challenges in environments with space constraints.
- Use of Scarce Resources: Certain types of solar panels incorporate rare elements. The process of sourcing and fabricating these materials can carry environmental repercussions.
Efficiency and reliability of solar energy
Over time, solar energy systems have witnessed remarkable improvements in efficiency. The term “efficiency” in the context of solar panels denotes the proportion of sunlight they can transform into usable electricity. Conventional silicon-based solar panels generally showcase an efficiency ranging between 15% and 20%, although premium panels can attain an efficiency rate exceeding 25%. Emerging technologies, including thin-film solar cells, promise to surpass these efficiency levels in the coming times.
When executed with precision and maintained diligently, solar energy setups prove to be notably reliable. The absence of moving components in solar panels minimizes the chances of mechanical disruptions. Nonetheless, regular upkeep in the form of cleaning and inspections is essential to facilitate peak performance. Moreover, solar energy systems can be complemented with battery storage units to ensure a steady electricity supply during diminished sunlight or grid failures.
Efficiency and reliability of wind power
The potency of wind turbines is quantified through their capacity factor, which illustrates the disparity between the actual electricity harnessed and the theoretical maximum output. Contemporary wind turbines usually exhibit capacity factors within the spectrum of 30% to 50%, although with refined designs, some manage to attain even loftier figures. Various factors, such as the velocity of wind, fluctuating air currents, and the phenomenon of wake effects, can influence the efficiency of wind turbines.
Wind power installations generally demonstrate commendable reliability and are engineered to endure diverse meteorological conditions. Maintaining optimal functionality and avoiding potential snags is imperative. Furthermore, to capitalize on the periods of heightened wind activity, wind power systems can be paired with energy storage mechanisms that retain surplus electricity, making it accessible during phases of reduced wind flow.
Cost comparison of solar energy and wind power
The expenses associated with installing solar energy and wind power systems can fluctuate, influenced by several factors like the scale of the project, geographical location, and available financial incentives. Generally speaking, the investment required for solar panels has been on a downward trend, thus making solar energy a more economical and reachable choice for many. Conversely, while the upfront costs of wind turbine installation might be steeper, they tend to have diminished running costs in the long run.
To conduct a comparative analysis of the costs associated with different forms of energy, the Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) is commonly utilized. This metric encapsulates the cumulative cost of setup, operation, and upkeep throughout the system’s lifespan and the electricity output. Solar energy’s LCOE has recently seen a brisk decline, positioning it as a viable rival to traditional energy forms in numerous territories. Wind power, too, possesses a competitive LCOE, especially in regions abundant in wind resources.
Environmental impact of solar energy and wind power
In the context of environmental conservation, both solar and wind energy overshadow traditional fossil fuel-dependent power generation methods. Solar energy emits no greenhouse gases or other harmful pollutants during its operational phase. Nonetheless, the manufacturing process of solar panels does entail some environmental consequences, primarily revolving around the extraction and refinement of raw materials.
Similarly, wind power stands as a clean energy avenue, devoid of releasing greenhouse gases or other pollutants during its operational phase. Yet, the creation and establishment of wind turbines bear some environmental ramifications, encompassing resource utilization and potential disturbances to local ecosystems. Despite this, it is broadly acknowledged that these impacts are substantially milder when juxtaposed with the pollution linked with fossil fuel-based power generation.
Final Thoughts
As we move steadfastly towards adopting more environmentally friendly energy alternatives, the comparison between solar power and wind energy becomes a focal point of discussions. As we steer towards a horizon less reliant on fossil fuels, it is imperative to comprehend the strengths and weaknesses of these two powerful options.
Solar power, a ray of optimism for numerous people, relies on plentiful sunlight to fuel our residences and commercial spaces. This medium symbolizes human innovation, leveraging the sun’s power with continually enhance efficiency and decreasing expenditures. Its straightforward setup and upkeep have garnered a following, especially in city and suburban areas.
Conversely, wind energy, characterized by its imposing turbines, utilizes the planet’s natural air currents to produce electricity. Although the initial establishment expenses may be slightly elevated, its minimal running costs and notable expansion potential present it as a strong alternative, particularly in areas blessed with steady wind patterns.
To sum up, both solar and wind energy possess the potential to spearhead a transition to a greener and cleaner future. Each comes with its benefits and challenges, yet their contributions to shifting towards renewable energy sources are indisputably critical. As conscientious residents of this planet, dedicating time to explore these renewable energy platforms thoroughly can equip us to make enlightened choices, laying the groundwork for a more luminous and pristine future for everyone.









