As the urgency for environmentally conscious and sustainable alternatives amplifies, renewable energy solutions, including solar power, are witnessing a surge in acceptance. Meanwhile, natural gas has steadfastly maintained a strong presence in the energy sector for a considerable duration.
Solar power stands as an abundant, financially viable, and perpetual resource. It utilizes the radiant energy from the sun, converting it into electric power in a lucid and lasting manner. Using this energy helps to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. On the flip side, natural gas, a fossil fuel category, finds extensive applications in various domains, such as heating, power generation, and diverse industrial activities. While it presents a relatively cleaner alternative than coal or oil, it’s pertinent to acknowledge that natural gas is associated with releasing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
Embark on this journey with us, where we dissect the merits and demerits of solar power and natural gas, analyzing facets like economic viability, environmental impacts, scalability, and effectiveness. You are equipped to make a sound decision that aligns with your values and necessities through a nuanced comprehension of the nuances associated with these energy forms.
Environmental impact of solar energy and natural gas
Solar energy is frequently recognized as one of the most eco-friendly energy sources accessible. It generates power without emitting any detrimental pollutants into the air. Solar panels function by capturing the sun’s rays, removing the necessity to burn fossil fuels. This dramatically diminishes carbon emissions and aids in battling global warming. Moreover, solar energy doesn’t create noise pollution, showcasing its environmental benefits.
Contrarily, natural gas, although less polluting than other fossil fuels, significantly impacts the environment. Natural gas combustion emits carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. Extraction practices, for instance, hydraulic fracturing or fracking, can potentially lead to adverse environmental effects, including water pollution and the destruction of habitats. Furthermore, the transportation and distribution process of natural gas may cause methane leaks, exacerbating the issue of greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, solar energy boasts a considerably lesser environmental impact in comparison to natural gas. It stands as a green and renewable energy option that can assist in minimizing our carbon footprint and alleviating climate change consequences.
Cost comparison between solar energy and natural gas
Examining the cost aspect, both solar energy and natural gas present their respective financial factors to consider. Setting up solar energy infrastructure demands a higher initial outlay compared to natural gas, encompassing the procurement and installation of solar panels and related machinery. Nonetheless, the price of solar panels has declined over recent years, gradually becoming more budget-friendly for homeowners and enterprises. Moreover, multiple financial schemes and governmental incentives can assist in alleviating the early costs associated with solar setups.
In contrast, natural gas is usually a more affordable option when stacked against other fossil fuels. It has served as a dependable and economical energy solution for a substantial period. However, natural gas pricing can be volatile, influenced by market dynamics and geopolitical elements. The burgeoning prominence of renewable energy alternatives and the heightened emphasis on diminishing greenhouse gas emissions have spurred initiatives for carbon pricing and regulatory measures, potentially affecting the future price trajectory of natural gas.
Comparing solar energy and natural gas requires a comprehensive view encompassing initial investments and prospective long-term savings. Solar energy holds the promise of substantial reductions in electricity expenditures over the years, with solar panels creating power that can reduce or even negate the necessity for electricity from the grid. Whereas natural gas, despite being more affordable at the onset, may not offer comparable long-term financial benefits as solar energy.
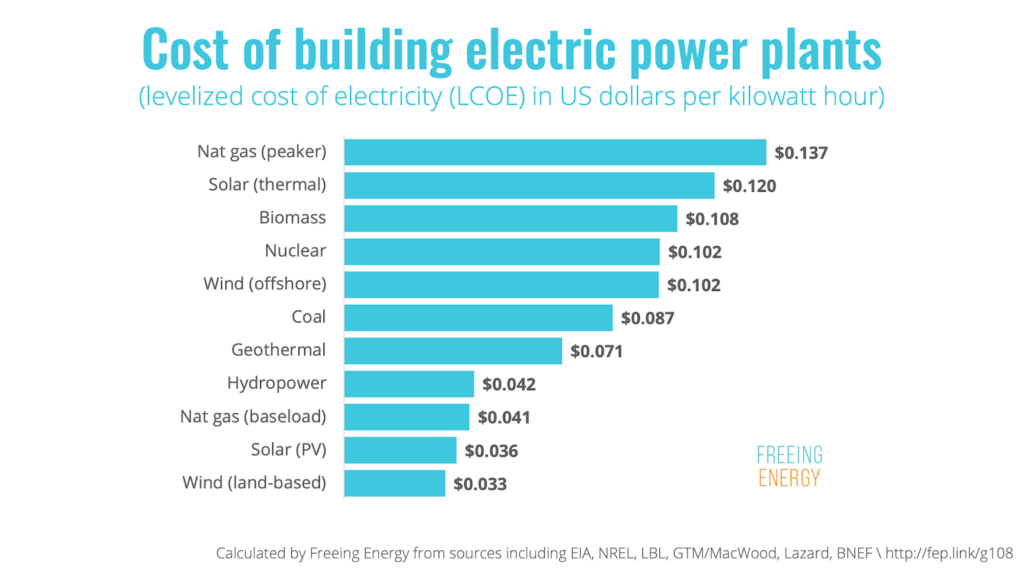
Credit: freeingenergy.com
Efficiency and reliability of solar energy and natural gas
Solar energy setups have witnessed remarkable improvements in efficiency throughout recent years. Contemporary solar panels can transform a significant fraction of solar radiation into electrical energy, optimizing the output. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of solar energy is closely tied to the availability of sunlight. Hence, it is notably more productive in locales with substantial sun exposure. Furthermore, the performance of solar panels might be influenced by elements such as obstructions, buildup of dust, and ambient temperature conditions.
Conversely, natural gas is celebrated for its substantial energy concentration and effectiveness. Its ease of transportation and storage earmarks it as a dependable energy source. Power plants utilizing natural gas can swiftly respond to fluctuations in electricity needs, thereby offering adaptability to the power grid. However, the processes of extraction and transit of natural gas might entail energy wastage, subsequently impacting aggregate efficiency.
In evaluating efficiency and reliability, a pivotal aspect is scrutinizing the precise demands of your energy consumption. Solar energy emerges as highly efficient in locales blessed with sufficient solar illumination, whereas natural gas presents steadfastness and agility in fulfilling electrical power necessities.
Availability and accessibility of solar energy and natural gas
Solar energy is fundamentally omnipresent and obtainable wherever sunlight pervades. It can be captured at varying scales, from individual residential solar installations to expansive utility-scale solar facilities. The reach of solar energy has further expanded due to the advent of community solar initiatives, enabling individuals and corporations to reap the advantages of solar power, even without appropriate roof spaces for solar panel installations.
In contrast, the reach of natural gas is not universally uniform. It requires a well-established infrastructure to facilitate extraction, conveyance, and distribution. Regions situated near natural gas deposits or connected to pipeline networks can conveniently access this form of energy. Conversely, areas lacking the necessary infrastructure for natural gas might encounter hurdles in adopting this energy variant for their respective needs.
When pondering the suitability of both solar energy and natural gas as potential energy providers, it is vital to take into account their ubiquity and accessibility in your particular geographical area.
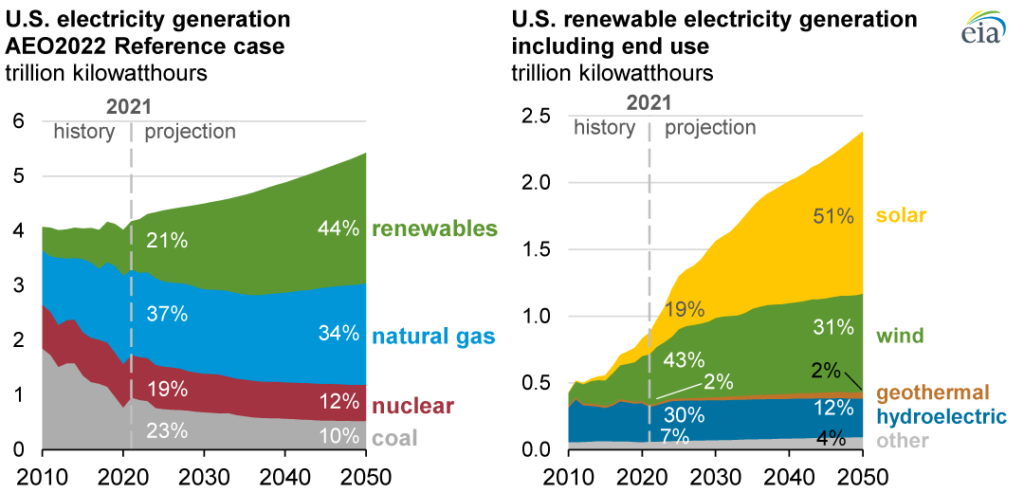
Credit: eia.gov
Government incentives and policies for solar energy and natural gas
Governmental incentives and policies are prominent in facilitating the increased use of renewable energy forms such as solar energy. Many regions and nations present tax alleviations, grants, and discounts for installing solar panel systems. These financial encouragements can mitigate the initial expenses, rendering solar energy a more accessible option for property owners and businesses. Additionally, various governments have implemented net metering schemes, where individuals with solar panels can sell surplus power back to the electricity grid, encouraging further solar power adoption.
Conversely, natural gas enjoys governmental endorsements in specific areas. Certain nations subsidize natural gas, thus presenting it as an economically viable alternative for users. Nonetheless, there seems to be a burgeoning movement of governments pivoting towards renewable energy forms and lessening the dependence on fossil fuels. This transformation in governmental stance could feasibly influence the scope of incentives available for natural gas in forthcoming times.
In evaluating solar energy and natural gas, maintaining an awareness of prevailing government supports and strategies in your locality is pivotal, as it can considerably influence the economic feasibility of employing these energy forms.
Long-term sustainability and future prospects of solar energy and natural gas
Solar energy holds a reputation for being a long-lasting and renewable source of energy, owing to its plentiful availability and renewable nature. The availability of solar energy remains as long as the sun radiates, providing a continuous source to tap into. Progress in solar technology, including the fabrication of more proficient solar panels and energy storage systems, augments the enduring viability of solar power. Given the escalating global emphasis on curtailing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to cleaner energy alternatives, solar energy harbors bright prospects for the future.
In contrast, despite being a vital source of energy at present, natural gas invokes certain apprehensions regarding its sustainability in the long haul. Being a fossil resource, natural gas reserves are finite and destined to deplete over time. Moreover, the processes involved in natural gas extraction and utilization lead to carbon emissions, consequently affecting the climate. Nevertheless, technological strides, such as carbon capture and sequestration (CCS), might potentially lessen the ecological impacts of natural gas utilization, prolonging its operational lifespan.
Ascertaining the enduring viability and impending prospects of solar energy and natural gas is crucial while making a knowledgeable choice concerning your energy supply.
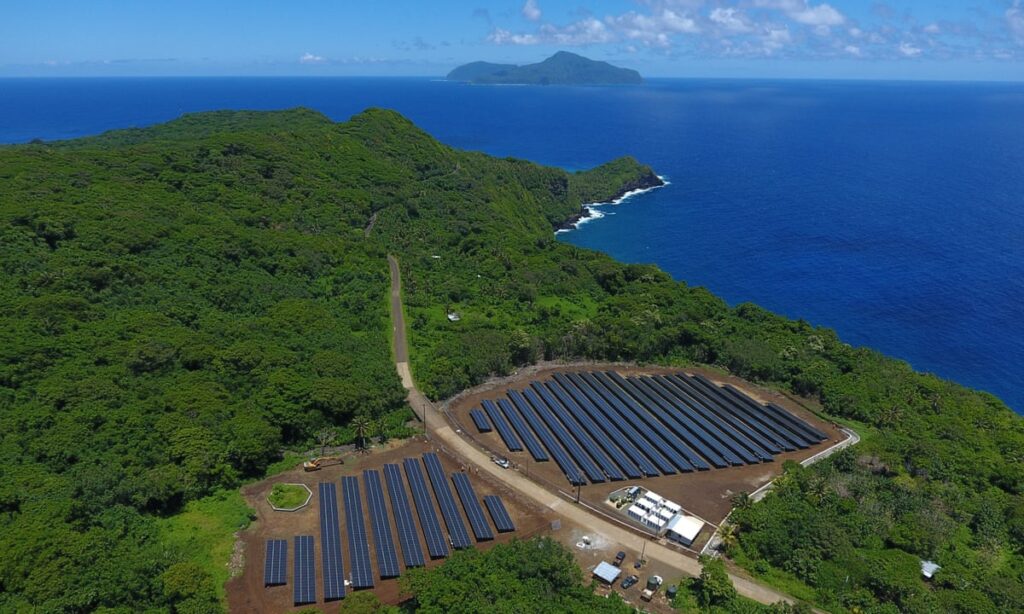

Credit: theguardian.com
Case studies and success stories of solar energy and natural gas implementation
Delving into real-world examples and triumphs can grant substantial perspective on the practical utilizations and advantages of solar energy and natural gas. There are many instances where solar energy has proven successful in residential and commercial sectors. One notable example is Ta’u Island in American Samoa. It revolutionized its power structure by incorporating solar panels and battery storage systems, allowing nearly the entire island to rely on solar power. Numerous enterprises and establishments have also embraced solar power, paving the way for reduced carbon footprints and diminished electricity expenses.
Similarly, using natural gas has permeated numerous sectors, encompassing power generation, heating, and transportation. Countries like the United States have witnessed a notable upsurge in the production and consumption of natural gas, fostering energy autonomy and enhancing the economy. Power stations running on natural gas have played a crucial role in supplying consistent electricity during times of peak demand, also facilitating the assimilation of fluctuating renewable energy resources into the power grid.
Examining these examples and success narratives, one can accrue concrete knowledge on the merits and hurdles tied to solar energy and natural gas, guiding you to a well-informed selection.
Considerations for choosing between solar energy and natural gas
Several considerations should be weighed when choosing between solar energy and natural gas. Initially, scrutinize your geographical location and the prevalence of sunlight and natural gas systems in the vicinity. You will find a broader spectrum of choices if your locality enjoys abundant sunshine and established natural gas networks. Subsequently, analyze your energy requisites and the extent to which each energy type can be scaled. The capacity of solar energy can be incrementally enhanced by incorporating additional panels, whereas augmenting natural gas usage may necessitate considerable upgrades to existing infrastructures.
Furthermore, ponder over your environmental objectives. Solar energy might be preferable if your focus is geared toward slashing carbon emissions and reducing environmental detriment. Conversely, natural gas could be a more fitting option if you emphasize reliability and adaptability.
Also, financial aspects hold a significant place in your decision-making process. Scrutinize the initial investments, enduring savings, and probable governmental incentives pertaining to both solar energy and natural gas in your locality. Calculate the projected return on investment and the duration for recovering the initial costs for both alternatives.
In conclusion, contemplate the forthcoming prospects and the enduring viability of both solar energy and natural gas. Factor in the advancements in respective technologies, government directives, and the global trajectory favoring renewable energy alternatives.
By meticulously considering these elements, you can make a choice that resonates with your personal beliefs, necessities, and long-term aspirations.






