The growing appeal of solar energy is undeniable. Solar energy stands out as the push for more sustainable and eco-friendly energy options gains momentum. This article sheds light on how solar energy fares economically against traditional energy means by providing relevant data and examples.
The Falling Cost of Solar Energy:
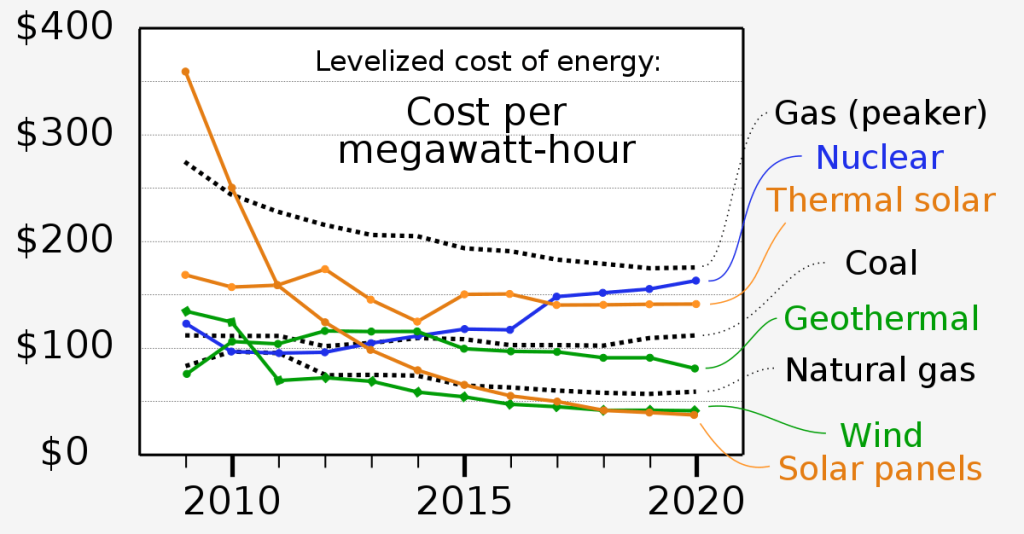
Solar energy rates have dramatically reduced over the last ten years. As the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) published, solar photovoltaic (PV) module expenses have experienced a decline of approximately 90% from 2010 onwards. The levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for large-scale solar endeavors experienced a decrease of 85% in the period between 2010 and 2021, qualifying solar power as one of the most budget-friendly energy sources available today.
Comparing Costs of Solar and Traditional Energy Sources:
In comparing the cost-effectiveness of solar to traditional energy methods, the LCOE, which represents the average cost of producing electricity over a technology’s lifespan, is vital. This covers initial setup charges, upkeep, and fuel costs. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2021, the average LCOE for large-scale solar PV ranged between $0.067-$0.180/kWh. In contrast, natural gas facilities had an LCOE of $56/MWh and coal plants at $42/MWh. These figures hint at solar energy being on par, if not more economical than its conventional counterparts.
Still, there’s more to the story. While LCOE provides a good starting point, it doesn’t encompass all factors. For instance, solar PV systems produce electricity mainly during the day, necessitating additional storage for nighttime usage. In contrast, fossil-fuel-powered plants run 24/7 and aren’t weather-dependent. Thus, even if solar appears cheaper on average, location and daily cycles might sometimes tilt the scale in favor of traditional energy sources.
Credit: wikipedia.org
Factors Contributing to the Decline in Solar Energy Costs:
Multiple aspects contribute to the reduction in solar energy expenses:
- Innovations in Technology: New materials, improved manufacturing techniques, and improved solar cells have made solar panels more effective and affordable.
- Scaling Benefits: Large-scale production has decreased solar panel and inverter costs as the solar sector expands.
- Support from Governments: Many nations have introduced tax breaks, grants, and other incentives to encourage solar energy use, lowering overall costs.
The True Cost of Conventional Energy Sources:
While the LCOE of conventional energy sources may appear competitive, it’s essential to consider their hidden costs. As externalities, fossil fuel extraction, transportation, and combustion have environmental and public health impacts. Fossil fuels release greenhouse gases and other pollutants, causing climate change, air pollution, and health problems. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated that global fossil fuel subsidies, including externalities, amounted to $5.2 trillion in 2017. Factoring in these hidden costs makes solar energy even more competitive.
Solar Energy and Grid Parity:
The point at which solar power’s cost equals or dips below that of traditional electricity sources is known as grid parity. Many places globally have reached this point, establishing solar energy as a cost-effective alternative for residential, business, and industrial initiatives. Solar energy is nearing grid parity in regions like California, Arizona, and Texas, leading numerous utilities to favor solar investments over conventional energy options due to its budget-friendliness and environmentally friendly benefits.
To sum up
As technology progresses, solar energy has evolved into a remarkably competitive alternative. The use of solar energy is becoming increasingly cost-effective, green, and job-creating as grid parity is achieved in more and more places. The future for solar energy appears luminous. Sustainable energy plans should embrace this clean, renewable resource now. Become a solar energy convert and contribute to a greener, more efficient tomorrow.







