Are you considering joining the increasing number of homeowners turning to solar energy to fulfill their household electricity demands? In this piece, we examine home solar setups, emphasizing the elements that combine to convert solar rays into electric power for your residence. Regardless of whether you are a veteran solar aficionado or a newcomer to this field, grasping the complexities of solar installations is vital to making well-informed choices.
Solar Panels
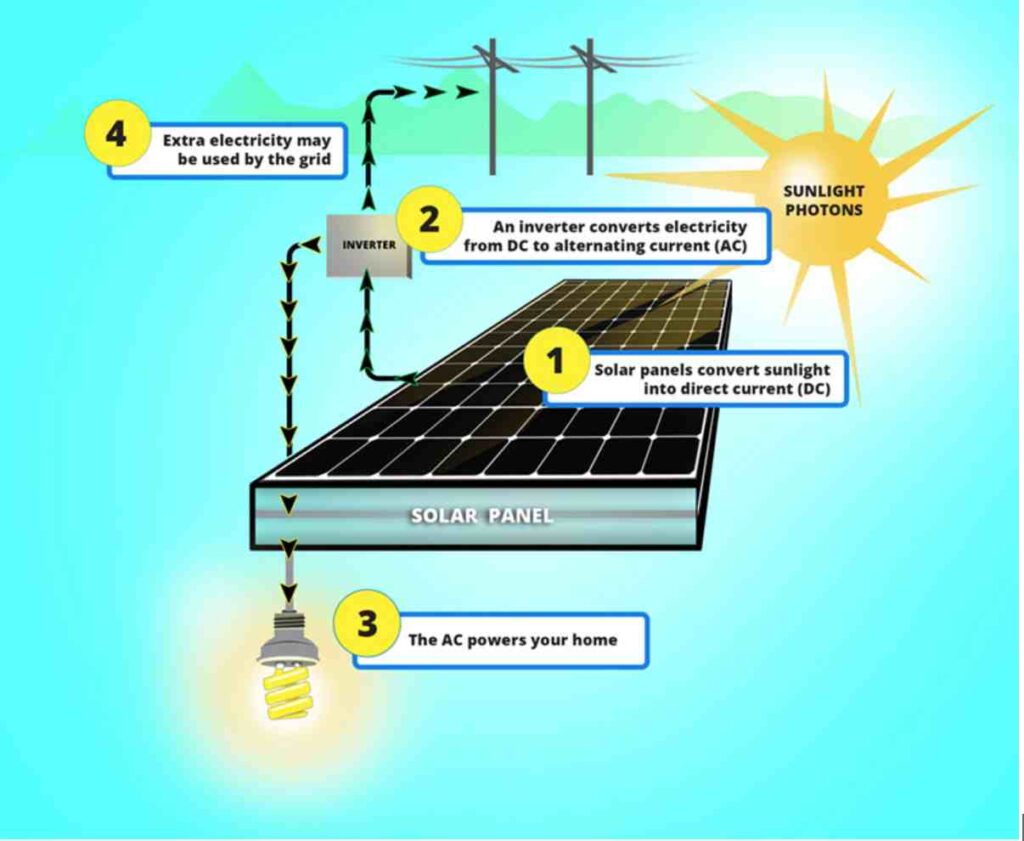
Credit: https://93energy.com/blog/how-solar-works
The cornerstone of any residential solar system is the solar modules. These modules contain photovoltaic (PV) cells that change sunlight into electric energy. This conversion occurs when sun particles knock electrons loose from atoms, initiating a stream of electricity. The effectiveness of solar modules in generating energy depends on various aspects, such as climatic conditions, positioning, and obstacles that result in shadowing. Throughout the day, these modules absorb the sunlight, converting it to direct current (DC) electricity that can be either used immediately or saved in battery storage systems. Nevertheless, to synchronize this DC output with your home’s alternating current (AC) setup, an inverter must modify the electricity into a format that can be spread throughout your home.
Solar Inverter

Credit: cleanenergyreviews.info
Though solar panels are a fundamental setup element, the inverter’s role is equally pivotal. Through the solar inverter, direct current (DC) emitted by the solar panels is converted into alternating current (AC), which powers your appliances. Inverters make electricity accessible since DC isn’t suitable for most household gadgets. This conversion is facilitated within the inverter, which processes the DC from one or several solar panels, translating it to AC that can be used instantly or preserved for future usage. The effectiveness of a residential solar setup significantly relies on the quality of its inverter.
Mounting System
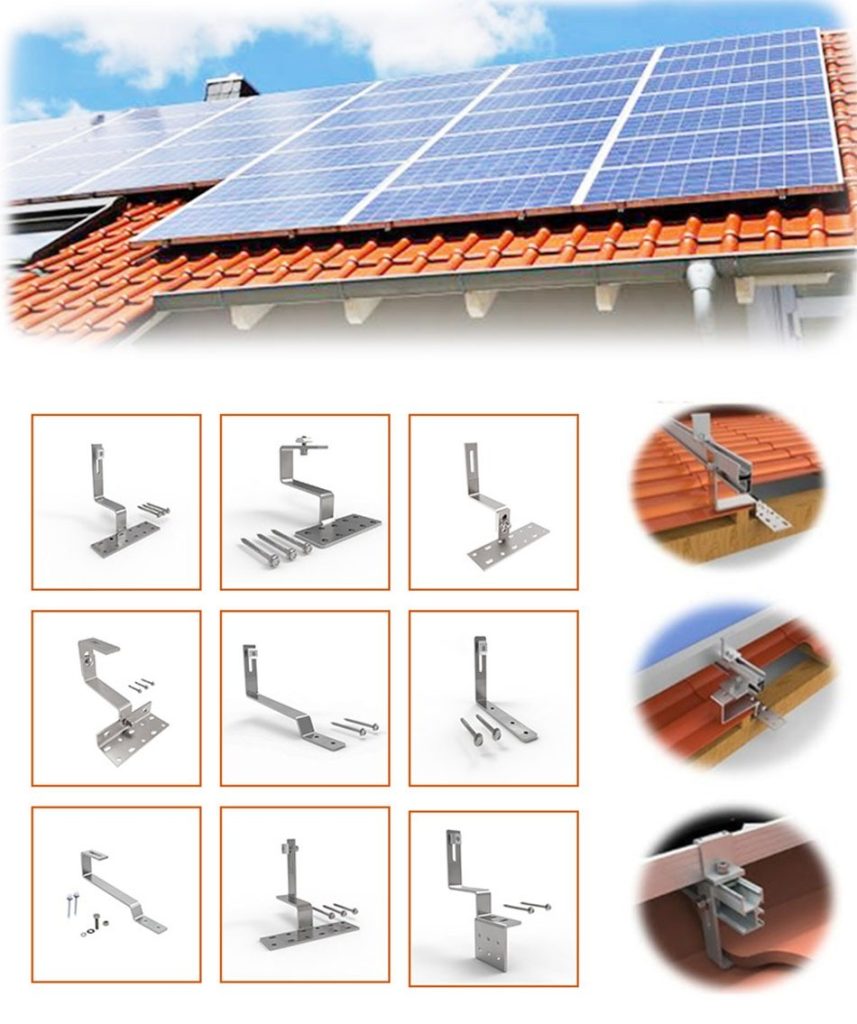

Credit: enfsolar.com
The mounting system is indispensable in securing the best exposure to sunlight. This structure affixes the solar panels to your roof or the ground, maintaining the correct alignment and inclination to maximize sun absorption. The alignment of your solar panels, which refers to the direction they face, is vital. For instance, orienting your panels to the south in the Northern Hemisphere grants optimal sunlight reception. Additionally, the tilt angle is vital in determining the extent of energy that can be harvested from direct sunlight exposure. Mounting systems allow for adjustments in both these aspects, ensuring optimal energy yield from your solar installation. Regardless of whether you opt for a roof or ground installation, the right mounting system is a linchpin in optimizing the energy output from your solar panels.
Solar battery

Credit: energy.gov
Homeowners who have installed a solar panel system may not be fully utilizing the potential of their home solar system without an accompanying energy storage solution. That’s where a solar battery comes in handy. Storing excess electricity generated by the panels during daylight hours ensures a consistent power supply even when sunlight is absent. A solar battery is a backup power source, providing much-needed electricity for household appliances and devices during power outages or when there is no sun to generate energy. This means homeowners with solar batteries don’t rely solely on grid electricity or generators to maintain their daily activities.
Charge controller
A charge regulator is crucial to any residential solar configuration, managing the electrical flow between the solar modules and the battery storage. Without voltage regulation, surplus energy can overpower the batteries, potentially causing them to overcharge or discharge at an accelerated rate, resulting in lasting damage and reduced battery lifespan. This is where the charge regulator steps in, ensuring an optimal amount of energy is channeled into your battery while safeguarding against over and undercharging, thus prolonging battery durability. Beyond battery protection, a high-quality charge regulator enhances overall efficiency by minimizing energy loss.
Electrical disconnects
Proper safety measures must be put in place to prevent accidents that may arise from electrical faults. One of the essential safety features of a home solar system is an electrical disconnect switch. An electrical disconnect switch is a safety mechanism that allows the homeowner or authorized personnel to manually shut down the solar system in case of maintenance or emergencies. It ensures that power stops flowing into your home, preventing potential hazards such as electrocution or fire caused by short circuits. During maintenance procedures, turning off the solar system’s power supply through an electrical disconnect switch is crucial since it lets you work on individual components safely without any risk.
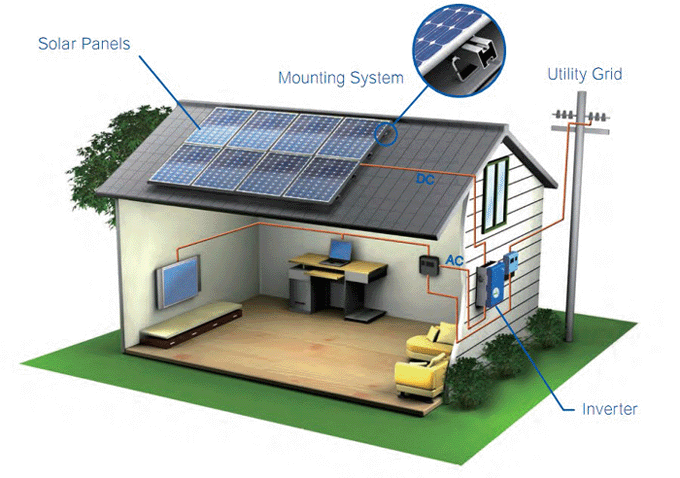
Credit: gogreensolar.com
Metering and monitoring equipment
These tools are instrumental in recording your solar modules’ performance and energy production levels, facilitating tracking efficiency across periods. The data gathered by these devices can offer significant perspectives on your system’s functioning standards. Analyzing this data lets you pinpoint any shortcomings or potential enhancements that could positively influence your setup’s efficiency. Moreover, diagnostic features available with many tracking and surveillance kits can aid in swiftly detecting and addressing emerging issues.
Cabling and Connectors
These components are vital for facilitating the flow of electricity across the system and establishing connections between solar modules, the inverter, battery banks, and other electric devices. A solar energy setup cannot operate without appropriate cabling and connectors. These electrical links ascertain a smooth and secure energy transition from one unit to another. Inferior or malfunctioning connectors and wires can result in voltage dips, diminished energy yields, and fire risks. Hence, allocating funds towards premium cables designed for integrating solar energy systems is essential. When choosing cables and connectors for your residential solar setup, numerous factors require consideration, including the dimensions of your PV setup, the gap between individual elements, and environmental factors such as variations in temperature or exposure to moisture.
Grid connection
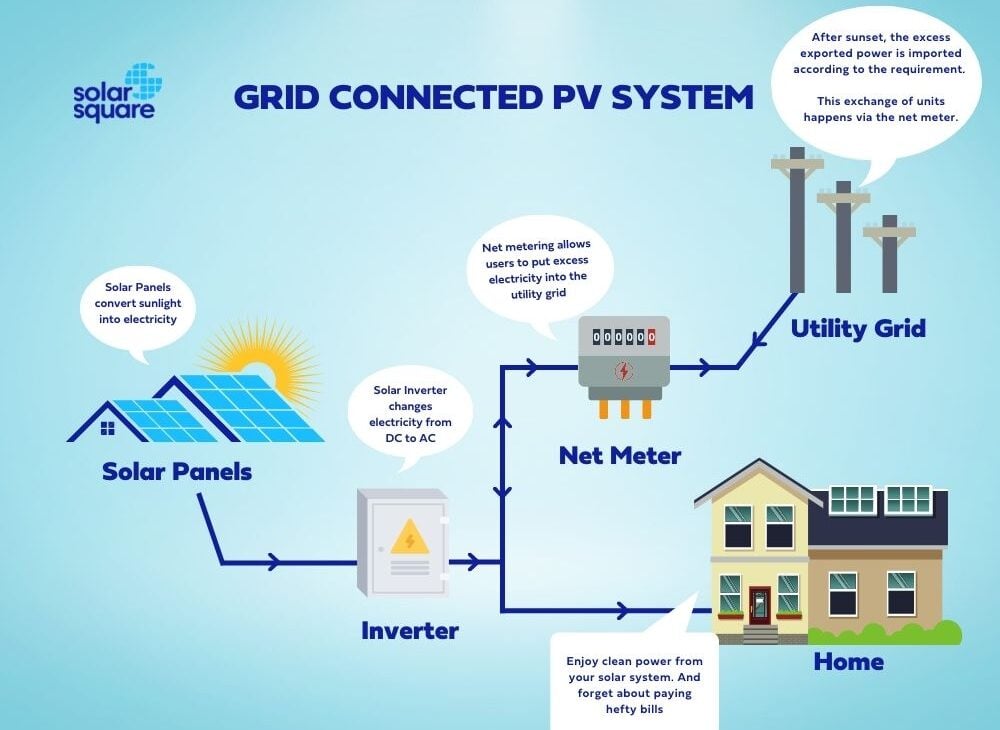
Credit: solarsquare.in
An integral element of a proficient home solar installation is the connection to the utility grid. This connection allows homeowners to channel surplus electricity generated by their solar modules back into the grid, often acquiring energy credits that can be utilized to reduce forthcoming energy expenses. This process of returning excess electricity to the utility grid is termed as net metering. When the solar installation at home produces more power than required, this additional energy is redirected back into the grid via the household’s linkage to the utility service provider. A specialized meter tracks the ingress and egress of electricity, rewarding homeowners for the extra energy they supply to the grid.
In Recap
To summarize, leveraging solar energy for your household’s necessities is an ecologically considerate decision and a prudent long-term investment. We’ve navigated through the principal components of a residential solar system, illuminating how they cohesively work to turn sunlight into usable electricity. With knowledge about these fundamental elements, from solar modules and inverters to battery setups and grid integrations, you can make educated choices on your journey toward solar energy adoption. As more individuals opt for solar power, we progress towards a more ecologically sustainable future. Therefore, let us persist in tapping into the remarkable energy of the sun, fostering a more pristine and luminous tomorrow for upcoming generations.









