As a green, renewable, and carbon-free alternative, solar energy is often hailed as the solution to our power problems. Analyzing the downsides of solar energy is crucial, however. While it undeniably presents many advantages, such as being eco-friendly and diminishing reliance on fossil fuels, several downsides aren’t frequently acknowledged.
A primary concern associated with solar energy is the steep upfront cost. Setting up solar panels and the requisite apparatus can pose a hefty expense, rendering it a less accessible choice for individuals with limited financial resources. Moreover, the efficacy of solar energy is contingent upon meteorological conditions. Therefore, it might not offer a constant energy supply compared to other energy sources.
Additionally, installing solar panels necessitates a generous amount of room, which could be impractical for smaller residences or areas with a high population density. Upkeep and cleaning of these panels might also demand considerable effort and resources.
In this discussion, we will delve deeper into these concerns to gauge if the merits of solar energy indeed surpass its conceivable downsides. We are better positioned to make informed choices about solar energy integration and maximize its potential by understanding all its facets.
The environmental impact of solar energy
Solar energy is frequently lauded for its favorable influence on the environment. It stands as a green and renewable source of power that doesn’t emit greenhouse gases during its operation. The technology captures the sun’s energy and transforms it into electricity, thereby being a preferable choice for those aiming to reduce carbon emissions.
Nonetheless, the creation and disposal of solar panels entail specific adverse environmental impacts. The manufacturing of these panels involves utilizing hazardous substances and leads to the release of greenhouse gases. Moreover, discarding solar panels can pose difficulties owing to their non-decomposable elements. Understanding solar energy’s environmental impact requires considering its entire life cycle.
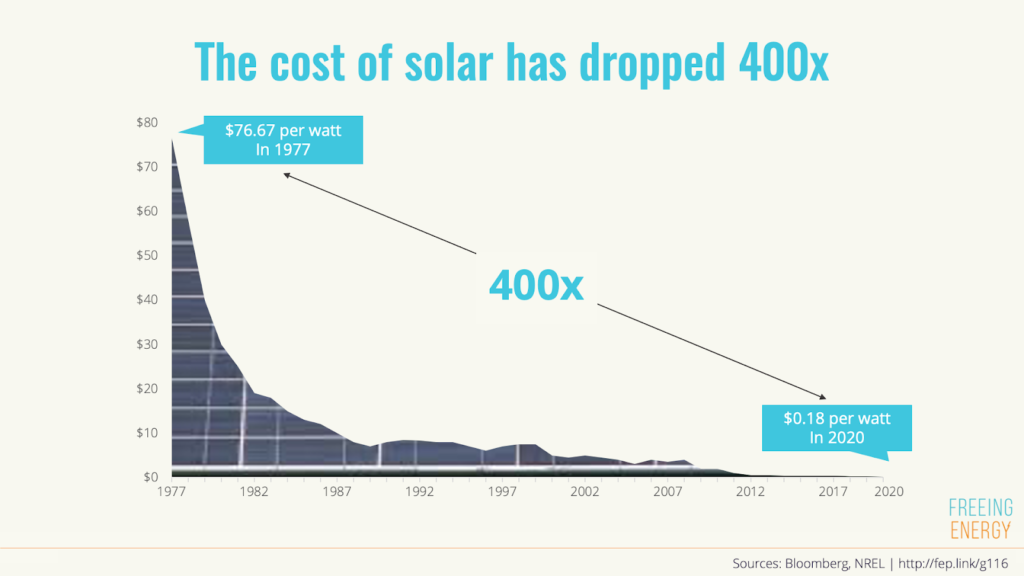
Credit: freeingenergy.com
The cost of solar energy
One of the most substantial obstacles to the broad acceptance of solar energy remains its initial hefty price tag. Installing solar panels and the essential gear can be financially taxing, potentially making it a less attractive choice for budget-constrained individuals. Although there has been a reduction in the prices of solar panels in the past few years, it continues to be a notable investment for a vast section of homeowners and commercial enterprises. This significant initial expense may discourage people and entities from transitioning to solar energy despite the prospective economic benefits in the long run. Thus, it is vital to critically assess solar energy’s financial aspects compared to its anticipated advantages.
Weather Dependencies
While solar energy presents a series of advantages, it is also accompanied by certain constraints that should be acknowledged. A primary constraint is its reliance on favorable weather conditions. Since solar panels necessitate direct sunlight to generate power, their effectiveness dwindles during overcast or rainy conditions. This emerges as a notable disadvantage, particularly in regions experiencing extended durations of adverse weather. Additionally, the productivity of solar panels decreases in the winter, characterized by shorter days and a lower solar angle. These constraints render solar energy somewhat less dependable when juxtaposed with alternative energy sources like fossil fuels or nuclear energy.
Maintenance and reliability issues
The process of upkeep and cleaning of solar panels can often be both time-intensive and financially demanding. Over the passage of time, elements like dust, grime, and debris tend to settle on the panel surfaces, consequently diminishing their output efficiency. Ensuring routine cleaning is essential to maintain peak performance, notably in locales characterized by elevated pollution or dusty surroundings. Furthermore, solar panels necessitate regular check-ups to identify potential damages or functional discrepancies. The costs associated with repairs or replacements further amplify the total expenditure on solar energy. These aspects concerning the maintenance and reliability of solar panels should be contemplated while assessing the viability of solar power systems.
Hurdles in Integrating with the Grid
Incorporating solar power into the existing electrical infrastructure harbors numerous obstacles. Solar power generation is intermittent, contingent on the presence of sunshine. This intermittency can engender difficulties in ensuring a consistent and reliable electricity supply. To counter this, energy storage solutions like batteries are frequently employed to retain surplus energy produced during sunny intervals for utilization during cloud-covered or nocturnal phases. However, the financial burden of these storage solutions might be too steep for a considerable segment of users. Moreover, merging solar power into the existing grid demands meticulous strategizing and collaboration, encompassing intricate technical and regulatory facets.

Credit: betterenergy.org
The impact on land use
The mounting of solar panels requires a substantial area, making them unsuitable for compact plots or regions with high population density. Undertaking large-scale solar energy initiatives often demands extensive stretches of land, potentially leading to environmental and societal repercussions. Solar farms could disrupt habitats and reduce biodiversity. Moreover, utilizing fertile agricultural lands for setting up solar facilities can influence the output of food crops. It becomes imperative to harmonize the drive for renewable energy resources with judicious land management to foster sustainable progress.
The future of solar energy
Notwithstanding its challenges, the allure of solar energy is augmented by ongoing technological progress to mitigate its existing restrictions. The pricing of solar panels is anticipated to experience a further dip, paving the way for an extended demographic of customers to afford them. Current research and development initiatives are centered on enhancing the performance and dependability of solar panels, along with the creation of novel energy retention systems. Looking ahead, solar energy is poised to assume a more prominent position in our energy framework, assisting in the transition towards a sustainable and carbon-conscious future.
FAQ
Can solar panels crack?
Indeed, solar panels are susceptible to cracking, typically due to severe weather phenomena like hailstones or direct physical impacts. Nonetheless, numerous panels are constructed to endure substantial wear and tear, boasting high durability. It is vital to ensure proper installation and consider implementing protective strategies to minimize the chances of cracking.
How long do solar panels last?
Generally speaking, solar panels have a substantial lifespan, lasting approximately 25 to 30 years. While there might be a marginal decline in their efficiency as years pass, they retain the capacity to produce a considerable quantity of electricity over a prolonged period. Regular inspections are beneficial to confirm their optimal functioning.
Do solar panels work in the winter?
Indeed, solar panels are operational during the winter months. Their functionality is dependent on sunlight rather than heat to produce electricity. Interestingly, their efficiency may actually elevate in colder climates as they function better at reduced temperatures. Nonetheless, their output declines during periods of snow coverage or during extensively short daylight hours.
Is Solar Energy Worth the Investment?
Approximating solar energy resources can prove to be a prudent investment. It facilitates the production of personal electricity, potentially resulting in significant savings over time. Moreover, as a renewable energy medium, it refrains from emitting detrimental substances that exacerbate climate change, thus serving as a sustainable option that benefits both the individual and the larger environment.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, it’s clear that while solar energy brings a beacon of hope in the transition towards cleaner and greener energy solutions, it’s not without its set of challenges. From the initial costs of installation to the reliance on sunny weather, these hurdles cannot be ignored. Furthermore, we must consider the space required for large solar farms and the production process of the panels themselves, which currently have a notable environmental footprint.
But remember, no source of energy is perfect. As we move forward, it is essential to work on these drawbacks, possibly turning them into strengths, steering our world towards a future that is not only brighter but greener. It’s an exciting journey that beckons the collective effort of every individual willing to make a difference. Let’s embrace solar energy’s possibilities with a realistic and informed perspective, making the best choices for our communities and our planet.









