Solar energy stands out in the journey towards a greener tomorrow in the fast-paced realm of green energy sources. Efficiently utilizing the sun’s energy is vital for both home and business utilities. One of the essential aspects of amplifying solar energy output is perfecting the tilt and positioning of the solar panels. Considering factors like geographic position, changes in seasons, and the distinct energy demands of a project, one can truly tap into the high capabilities of solar energy systems.
This piece elucidates the significance of the solar panel angle and direction, offering valuable perspectives and advice to assist you in making well-informed choices for your solar setup. Let’s venture into the sphere of solar energy fine-tuning and learn how to fully harness this plentiful, eco-friendly, and renewable power source.
Solar Panel Orientation
What is it?
In basic terms, solar panel orientation means the direction in which the panels are pointed. This orientation is pivotal because it dictates how much sunlight the panel receives and thus impacts its energy output. Solar panels must be positioned so that they catch the most sunlight throughout the day, taking into account the sun’s trajectory. You can significantly improve your solar energy setup’s efficiency and performance by carefully determining and tweaking the solar panel’s orientation.
Optimal orientation for different geographic locations
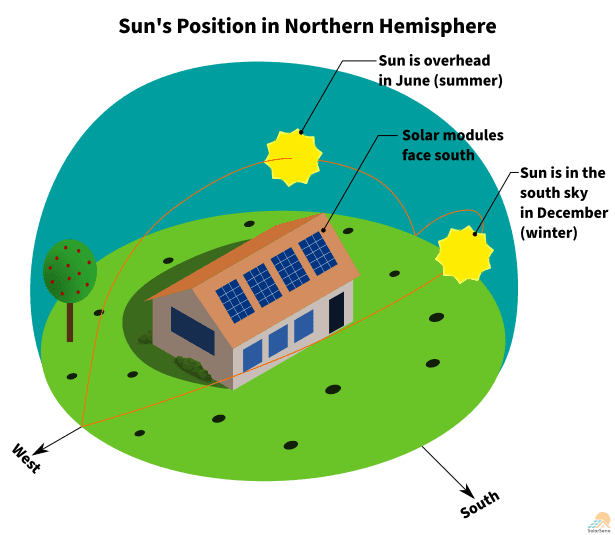
Northern Hemisphere
In the Northern Hemisphere, the optimal orientation for solar panels is generally south-facing. This is because the sun follows a path across the southern part of the sky throughout the day. Positioning solar panels to face south ensures they receive the maximum sunlight, thus maximizing energy production. The angle at which the panels should face south may vary depending on the location and latitude.
Southern Hemisphere
It is typically best to have the solar panels facing north in the Southern Hemisphere. This positioning guarantees the highest exposure to sunlight during the day since the sun mainly traverses the northern section of the sky. Setting up the panels with a north-facing orientation allows them to harness sunlight more efficiently, thereby improving energy generation and the system’s overall performance.
Equatorial regions
In regions near the equator, where the sun remains almost directly above throughout a significant part of the year, the ideal orientation for solar panels would be either true north or true south. This orientation guarantees that the panels are illuminated evenly during the day as the sun arcs across the sky. Arranging the panels along the east-west axis and positioning them at a tilt angle matching the location’s latitude optimizes sunlight reception, yielding greater energy output. Additionally, this alignment helps in reducing shadowing effects and facilitates steadier solar power generation across various seasons in equatorial zones.
Credit: solarsena.com
Impact of shading and obstructions on orientation
Shadows and blockages can significantly affect the efficiency of solar panels since they diminish the quantity of sunlight that can reach the panels. Even a minor shadow on one panel can significantly decrease energy generation for the whole setup, particularly for panels that are connected in series. To lessen these impacts, it’s crucial to meticulously evaluate the location and steer clear of or minimize barriers like trees, buildings, or other edifices that might project shadows onto the panels. Correct orientation, which considers potential shading factors, maintains the best possible sunlight exposure, thus enhancing your solar energy system’s effectiveness and production rate.
Orientation adjustments for seasonal variations
Adjusting the solar panels’ orientation for seasonal shifts means altering the direction they face to accommodate the sun’s varying path in the sky over the year. As the Earth orbits the sun, the sunlight’s angle of incidence changes, influencing the amount of solar energy captured. You can maximize energy generation by tweaking the solar panel’s direction to more squarely face the sun during specific seasons. For example, in the Northern Hemisphere, during summer mornings, panels should be angled a bit towards the east and, during winter afternoons, a tad towards the west. This ensures they capture the most sunlight throughout the entire day.
Solar Panel Angle (Tilt)
What is it?
Solar panel tilt angle refers to the angle at which solar panels are inclined relative to the ground. It plays a vital role in maximizing efficiency by guaranteeing the panels receive the most direct sunlight possible. A well-optimized tilt angle considers factors like latitude and seasonal sun path variations, allowing the panels to capture sunlight more effectively throughout the year. Adjusting the tilt angle can significantly increase solar energy production, making your system more efficient and cost-effective.
Credit: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Factors influencing optimal tilt angle
Latitude
Latitude is critical in determining the optimal solar panel tilt angle for maximum efficiency. As the angle between the Earth’s surface and the sun’s rays varies with latitude, adjusting the panel tilt to match the local latitude ensures maximum sunlight exposure. Generally, a higher latitude requires a steeper tilt angle, while a lower latitude calls for a shallower tilt. The optimal tilt angle is roughly equal to the latitude of the installation site. This angle helps to align the solar panels perpendicular to the sun’s rays at solar noon when the sun is at its highest point in the sky. Accounting for latitude helps solar panels receive direct sunlight throughout the year, optimizing energy production and ultimately enhancing the overall performance of the solar energy system.
Seasonal variations
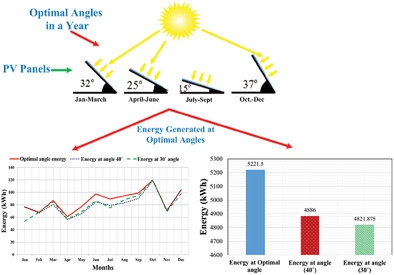
Solar panel tilt angle seasonal variations are adjustments made to the angle of solar panels throughout the year to maximize efficiency. These adjustments account for changes in the sun’s position in the sky due to Earth’s axial tilt. In summer, tilting panels at a lower angle maximizes exposure to the higher sun, while in winter, a steeper angle captures sunlight from the lower sun. Periodic adjustments help maintain optimal energy production, ensuring your solar energy system performs efficiently throughout the year.
Solar panel application (residential, commercial, utility-scale)
Their application strongly influences the tilt angle of solar panels. Residential installations often conform to roof pitch, prioritizing aesthetics and space constraints. Commercial systems may allow for greater angle customization, targeting energy generation peaks during business hours. Utility-scale projects focus on maximizing energy output and may employ tracking systems or adjustable tilt angles to optimize performance throughout the year, taking full advantage of the available land and solar resources.
How to calculate the optimal tilt angle
Calculating the optimal tilt angle for solar panels involves considering the latitude of the installation site. As a general rule, the tilt angle should be equal to the latitude for year-round energy production. However, to account for seasonal variations, add 15 degrees during winter or subtract 15 degrees during summer for improved efficiency. Online solar calculators and smartphone apps are also available to help determine the best tilt angle for your specific location and requirements.

Credit: solarsena.com
Fixed tilt vs. adjustable tilt systems
Fixed tilt systems have solar panels mounted at a fixed angle, optimized for average annual sunlight exposure. They are cost-effective and low maintenance but may not capture peak sunlight throughout the year. Adjustable tilt systems allow for angle modifications, adapting to seasonal variations in the sun’s position, thus improving solar energy capture. While adjustable tilt systems can enhance efficiency, they come with higher installation and maintenance costs than fixed-tilt installations.
Tracking Systems
Credit: sciencedirect.com
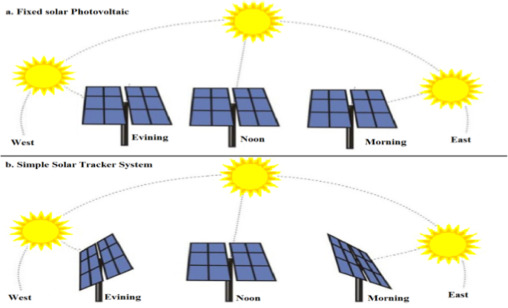
Advanced solar technology, known as tracking systems, aims to enhance solar energy production by maximizing the efficiency of solar panels’ angle with the sun’s position during the day. Two categories of tracking systems exist: single-axis and dual-axis.
Solar panels in single-axis tracking systems are rotated along a fixed axis, generally positioned north-south. By doing so, the panels can efficiently track the sun’s movement from east to west, resulting in increased sunlight capture compared to unmoving installations. These systems are affordable and particularly suitable for expansive solar farms.
Alternatively, dual-axis tracking systems grant solar panels two degrees of motion, meaning they can rotate horizontally and vertically to track the sun’s path as it moves in both directions and changes elevation. Although these systems generate more energy than single-axis trackers, they are also more intricate and expensive.
Both tracking systems can significantly improve solar energy production compared to fixed installations, but their suitability depends on location, budget, and project scale.
To sum up
Optimizing solar panel angle and orientation is crucial for maximizing energy production, as it ensures panels capture the most sunlight throughout the day, significantly enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of solar energy systems. Seeking professional advice for optimal solar energy production is essential, as experts can assess your specific needs and location, ensuring maximum efficiency and return on investment for your solar installation.









